Universal Design for Learning
Anne Hayes, Independent consultant on inclusive education

Accessible Digital Textbooks Using Universal Design for Learning for children with and without disabilities
What is UDL?
UDL is an educational framework recognizing that all children learn differently and benefit from differentiated learning techniques in the classroom. Essentially, UDL uses practices, space and materials that engage all of the learning strengths mentioned above. UDL seeks to accommodate individual learning differences and styles by developing and making use of flexible learning environments. Such approaches particularly accommodate children with different types of disabilities and facilitate their inclusion in the classroom.
Moving away from the ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach to learning improves learning outcomes for all children, whether or not they have disabilities, and improves students’ motivation to learn.
UDL merges neurosciences and learning science

|
Brain networks
|
UDL principles
|
|
Affective networks enable students to engage with the environment consistent with their emotions and proactivity |
Multiple means of engagement—the “why” of learning. How students are best motivated to learn.
|
|
Recognition networks enable students to perceive and understand input. |
Multiple means of representation—the “what” of learning. How students best receive information or learn information.
|
|
Strategic networks enable organization, action planning, implementation, and self-monitoring.
|
Multiple means of action and expression—“the “how” of learning. How students best express knowledge and what they have learned.
|
Source: CAST.org, 2018
Framework
Source: CAST.org
UDL and technology

UNICEF and its partners are committed to addressing all three challenges to promote equitable learning opportunities for learners with disabilities. This guidance document is a first but important step to help educational systems move towards providing more accessible learning materials.
Technology can be a powerful tool for applying UDL principles in a classroom as it allows students to learn through:
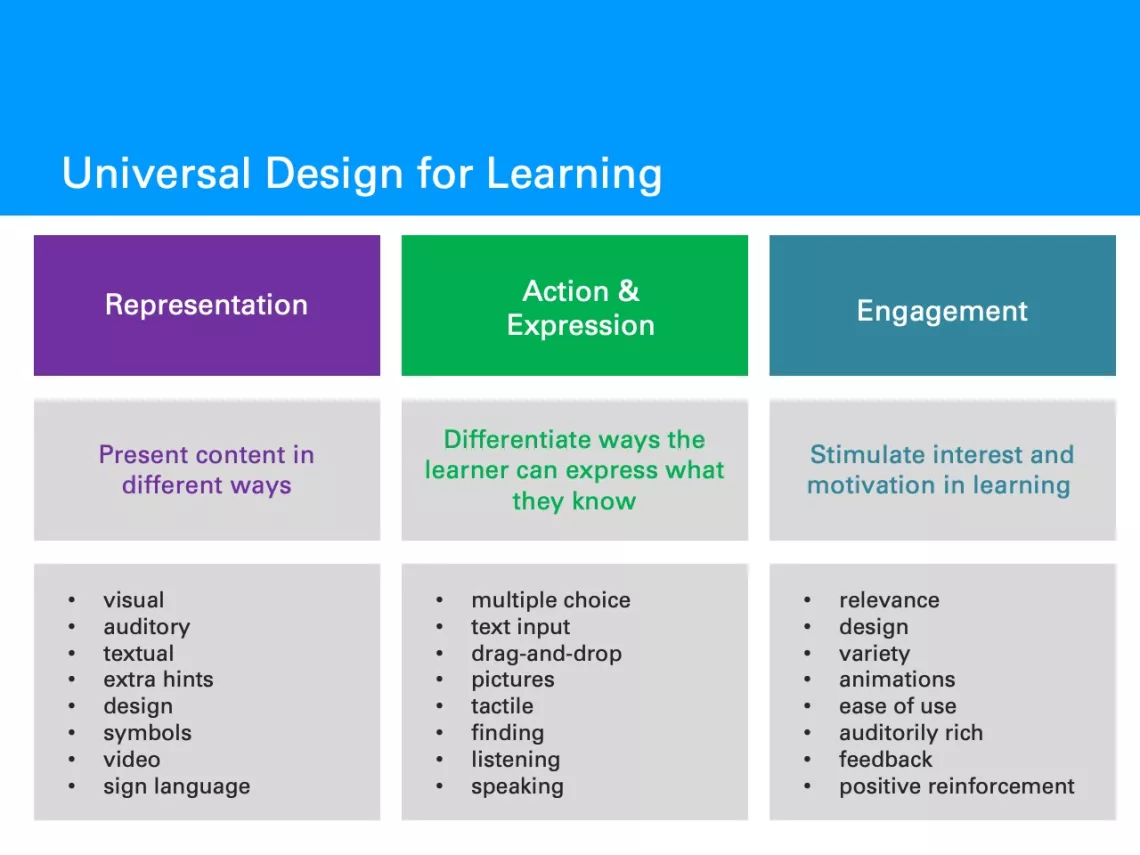
- Multiple means of representation. This signifies that children perceive and comprehend information differently. For example, some children learn better by having access to visual aids while other children may require auditory reinforcement. Multiple means of representation allow students to learn using options for perception, language and symbols, and comprehension. This would include, for instance, providing videos with captioning or audio transcriptions, allowing learners who are deaf and/or have language processing disorders to access the information provided in videos.
- Multiple means of expression. Students express learned information in different ways. As stated by the National Center on Universal Design for Learning, “It should also be recognized that action and expression require a great deal of strategy, practice, and organization, and this is another area in which learners can differ. In reality, there is not one means of action and expression that will be optimal for all learners; providing options for action and expression is essential” (CAST, 2018).
- Multiple means of engagement. Students are motivated and engaged in learning in different ways. This principle encourages students to explore individual interests or learning methods. For some, this might be watching instructional videos, while for others, this might be doing interactive exercises to demonstrate knowledge. Developing textbooks that allow multiple means of engagement supports the learning of all children.
UDL framework applied to technology for textbooks and learning materials
Impact of accessible digital textbooks using UDL

- Improves access and retention
- Improves literacy and learning for all students
- Improves joyful learning through interactive learning materials
- Enhance teacher capacity and support
- Enhance parental engagement in learning
- Promotes more inclusive and quality learning environments







